Seamless Manufacturing Solutions (Video)
Discover exatcly what Batten & Allen's full-service offering entails and how it will positively impact your project...
Brands are choosing us to partner with them to bring innovate products to market quickly and cost effectively.
Working on a Prototype and need expert input, why not get in touch and talk with our experts.
Poor or inconsistent solderability has expensive consequences. It leads to line stops – and worse: what if finished products with compromised solder joints get out into the field? And fail.
Solder joint failures in the field are not acceptable in any industry but in certain sectors they can have life-critical repercussions – such as in aerospace, medical or automotive electronics.
Solderability issues can be among the most difficult quality problems facing manufacturers. They call on us to troubleshoot their component challenges and provide advanced plating solutions.
Carrying out cutting-edge experimentation and research is one of the key factors that sets Batten & Allen apart from our competitors…
A solder joint failure in the field has expensive consequences in more ways than one. Aside from the obvious damage to the product and the supplier’s/OEM’s reputation, there is all the time (and therefore money) spent on:
Failures in the field could mean hundreds of hours of investigation. You could be looking for the proverbial needle in a haystack – a moving needle if the technical problem or quality inconsistency is caused by an intermittent fault.
And all with the frustrating realisation that the solderability issue could be merely one symptom of a far deeper quality control malaise that stemmed from buying too cheaply or from cutting corners. So even if the OEM/supplier successfully traces the one particular fault reported to them, there’ll always be the nagging doubt that other gremlins could be waiting in the wings…
Faced with the worrying time and cost of troubleshooting and solving these solderability problems, OEMs and their suppliers seek expert help from Batten & Allen.
Purchasers, specifiers and engineers turn to us because they don’t have the specialised expertise or experience required to analyse very small plated and stamped electronics components at a sub-micron level.
And they don’t have the time. It could take them hundreds of hours to accomplish a task that our plating engineers could handle quickly and easily because it is our specialist area of expertise.
Using lasers and X-rays, our engineers carry out precision micro-sectioning of parts, examining them under a 1,000x microscope to investigate the layers (from 0.1μm to 6-10μm) to identify any issues that could affect solderability.
Many of the solderability issues we are called on to solve involve non-wetting or insufficient wetting during multiple heat excursions required for reflow.
Non-wetting on surface mount or through-hole components will leave weak joints that do not form a strong bond with the board. Anything less than 100% wetting – with no gaps or spaces – risks leaving a poor connection.
Batten & Allen is certified to ISO 9001:2015, IATF 16949:2016 (Automotive Quality Certification) and ISO 14001:2015 (Environmental Management). Other certifications include REACH, RoHS and CFSI (Conflict-Free Supply Chain).
Our engineers control the plating process in real time to ensure high quality thickness that provides good solderability. This, along with higher levels of quality assurance, enables us to prevent issues before they occur – ensuring reliability, even in very high volumes.
Plating technology has taken a huge leap forward in recent years – improving efficiencies and enabling vastly superior monitoring and manipulation of the electroplating process.
The SCADA/HMI system on our new reel-to-reel electroplating equipment gives our expert engineers easy at-a-glance access to a wealth of real-time data.
At the heart of the equipment is software-based programme logic controller (PLC) technology which enables greater productivity and detailed reporting – resulting in optimised operations and greater overall system flexibility. Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) technology maintains efficiency and uptime.
All this technology enables our engineers to control the plating process more precisely – producing higher quality components with:
Contact Batten & Allen for expert technical help to troubleshoot solderability issues affecting the quality, consistency and deliverability of your new and existing projects.
Discover exatcly what Batten & Allen's full-service offering entails and how it will positively impact your project...
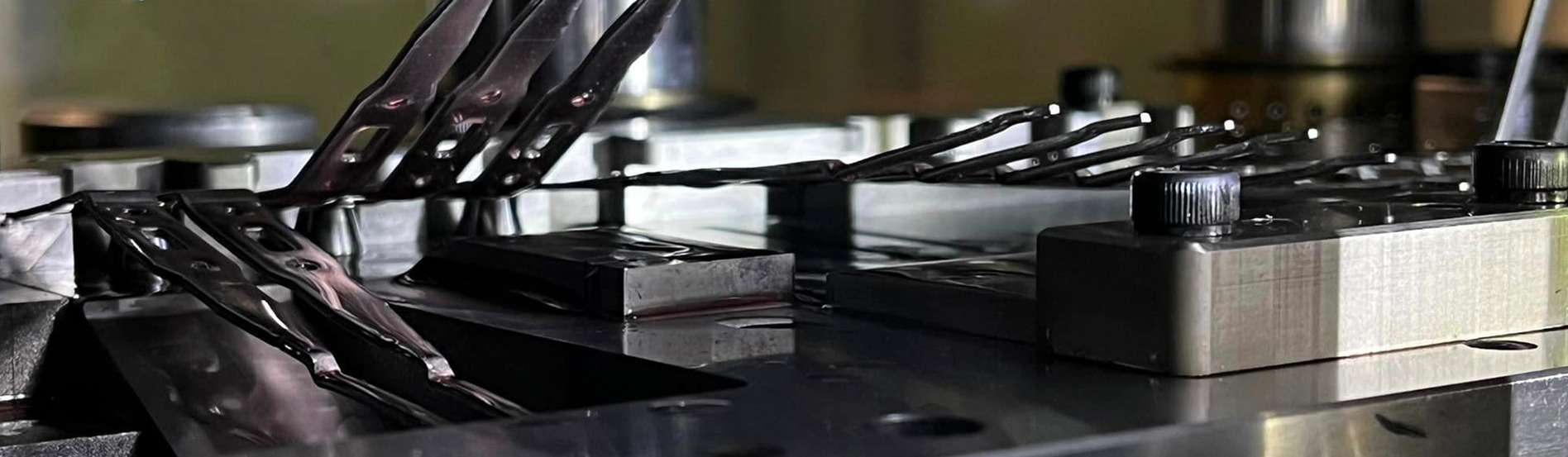

To discuss your turnkey solutions with our expert team please get in touch.

In today’s world of manufacturing, turnkey solutions have become a key methodology in promoting efficiency and delivering successful projects.